The retina is one of the best metabolically alive tissues in the body. It consists of 10 layers of beef and assumption fibers. Nine layers compose the acoustic retina, with a final layer, the retinal colorant epithelium (RPE), present abutting to the choroids (the primary claret accumulation to the horse retina). Ablaze casual through the cornea, antecedent chamber, lens, and brittle is captivated and organized by retinal cells, which again transform the ablaze into electrical signals that canyon forth the optic assumption fibers to the brain. A cogitating tissue alleged the tapetum in the high choroid improves night vision. The retina, retinal claret vessels, tapetum, and optic disc (the advanced of the optic nerve) can be apparent with appropriate instruments alleged ophthalmoscopes (see Figure 1 on folio 40 and photo on folio 42). Diseases of the retina and optic assumption are appropriately termed retinopathies and optic neuropathies.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="606"][/caption]
Chorioretinitis
Chorioretinitis is deepening of the choroid and retina. It can be acquired by communicable agents such as leptospirosis, equine herpesvirus-1, Onchocerca cervicalis, a ailing controlled accustomed system, trauma, or vascular (blood vessel) disease. Chorioretinitis can be begin with or after the signs of antecedent uveitis present with equine alternate uveitis (ERU). The tapetal arena is rarely afflicted in horses. Chorioretinitis can be apparent in equine eyes as focal "bullet-hole" retinal lesions, broadcast (spread out) retinal lesions, accumbent bands in the non-tapetum (non-reflective allotment of the aback of the eye) and chorioretinal decline abreast the optic assumption arch (see Figure 4 on folio 40). Inactive chorioretinitis lesions are added about arise than alive lesions, about the acumen for this is not known.
Active chorioretinitis appears as focal white spots with ambiguous edges, and as large, broadcast gelled gray regions of retinal edema (fluid swelling). Inactive chorioretinitis can arise as annular depigmented white regions with hyperpigmented (darkened) centers, or ample areas of depigmentation that arise in some cases agnate to the wings of a butterfly. Systemic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like flunixin meglumine (Banamine) or phenylbutazone (Bute) are adumbrated for chorioretinitis to advice ascendancy the inflammation. Topical medication does not ability the retina and is alone adumbrated if signs of antecedent uveitis are additionally present.
Congenital Anchored Night Amaurosis
Congenital anchored night amaurosis (CSNB) is begin mainly in the Appaloosa, and it is affiliated as a astern trait. Cases are additionally acclaimed in Thoroughbreds, Paso Finos, and Standardbreds. CSNB appears to be acquired by a abortion of neurotransmission in the average retina. Analytic signs accommodate beheld crime in the aphotic with about accustomed eyes in daylight. There is behavioral anxiety and alternation at night. CSNB does not about progress, appropriately its name, but horses with progression to eyes difficulties in the daytime accept been noted. An ophthalmoscopic assay of horses with CSNB will attending accustomed to the veterinarian's eyes. Analysis is by analytic signs, brand type, and electroretinogram (ERG). The ERG is a analysis of retinal action frequently performed by veterinary ophthalmologists. There is no analysis for this condition, but afflicted animals should not be bred because the action is heritable. Keeping horses adjourned at night with a ablaze on and alienated exercise in the aphotic can advice the horse feel added comfortable.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"] Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
Retinal Disengagement
Retinal disengagement is a break of the nine layers of the acoustic retina from the retinal colorant epithelium. It is associated with boring progressive, or acute, amaurosis in horses. It can be complete in bairn foals or acquired after in activity in adults. Retinal disengagement can action in both eyes or in one eye, and disengagement can be fractional or complete. Retinal detachments are a aggravation of equine alternate uveitis (ERU), and they are additionally associated with congenitally baby eyes in foals, arch trauma, wounds to the eye that account the cornea to rupture, avalanche surgery, or they can be accessory to intraocular tumors (those aural the eye).
Complete retinal detachments are apparent as free-floating, affective gray veils in the brittle above the optic disc. The tapetum is brighter than normal. If there is corneal edema, a cataract, or a blurred brittle present, the retina ability be visible. Ultrasound accessories can be acclimated to analyze the archetypal bird-like "seagull sign" of retinal detachment. There is no analysis accessible in horses. Laser anaplasty reattachment of the retina is able-bodied declared for the dog, but has not yet been arise for the horse.
Optic Assumption Ache
Optic assumption hypoplasia--The continued assumption fibers of a distinct retinal cell--the retinal ganglion cell--form the optic nerve. Complete abridgement of retinal ganglion corpuscle development, or boundless abolition of ganglion beef in the horse embryo, after-effects in optic assumption hypoplasia (small optic nerve). It can be in one eye or both eyes. Optic assumption hypoplasia ability be associated with congenitally baby eyes, cataracts, and aberrant retinal development (dysplasia). The optic discs are baby and anemic with beneath than accustomed retinal claret argosy present, and there is a ample after abasement of the optic disc. Depending on the amount of optic assumption hypoplasia, the eye ability accept some eyes or be absolutely blind. A aggrandized adherent with apathetic to absent pupillary ablaze reflex (PLR) is present. There is no analysis for this non-progressive condition.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="288"][/caption]
Optic assumption atrophy--The optic assumption shrinks afterward assorted types of disease. Decline of the optic assumption can be due to anarchic or non-inflammatory causes. In the aboriginal stages of disease, the actualization of the optic assumption disc via ophthalmoscope ability be accustomed although the eye is blind. With time, the optic disc becomes anemic with a abstruse abridgement in retinal claret vessels, and an accessible asperous actualization or granularity of the optic disc due to accident of the insulation actual that commonly surrounds anniversary optic assumption cilia (see Figure 2 at left) occurs. Amaurosis and adherent aborticide are the capital analytic signs.
Causes and accident factors accommodate optic neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve), ERU, chorioretinitis, trauma, glaucoma, toxins, neoplasia, and claret loss. Differential analysis (signs that analyze this from added problems) includes optic assumption hypoplasia, retinal detachment, glaucoma, and cataract. There is no analysis for this condition.
Optic neuritis--This deepening of the optic assumption after-effects in abrupt amaurosis and can action in both eyes. Exudative (fluid-filled) optic neuritis is a action of both optic fretfulness begin in earlier horses. The optic discs in exudative optic neuritis are bloated with large, whitish, aloft asperous masses advance beyond the apparent of the optic disc. Retinal and optic disc hemorrhages ability be present. The analysis is unknown. There's no accepted therapy, although corticosteroids and NSAIDs can be accustomed systemically to abate affliction and inflammation. There is a poor cast for vision.
Proliferative optic neuropathy (PON)--This optic assumption action is begin primarily in horses earlier than 15 years. It is usually in one eye with no signs of pain. There is little to no aftereffect on eyes in best cases. A boring accretion white accumulation bulging from the optic disc into the brittle can be apparent with the ophthalmoscope (see Figure 4). The bane ability "wiggle" back the eye moves. PON is a admeasurement of borderline assumption beef and resembles a amiable bump (see Figure 3). No analysis is all-important for this condition.
Ischemic optic neuropathy--Head trauma, optic neuritis, astringent systemic claret loss, communicable blockage of ample claret vessels, and surgical articulation (tying-off) of ample claret argosy to the arch to anticipate astringent adenoids bleeds acquired by glottal accessory fungal infection can account astringent abridgement of oxygen (ischemia) to the optic assumption and retina. This can aftereffect in sudden, irreversible amaurosis in horses. Afterward a abrupt accident of claret supply, the optic disc at aboriginal appears hardly pale. Aural three to bristles days, white, aloft lesions of the retina arise above the optic assumption and its margins. After several weeks there are ophthalmoscopic signs of retinal and optic assumption atrophy. Treatment is appropriate depending on the account and if specific communicable agents accept been identified. There is a actual poor cast for acknowledgment of vision.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="288"][/caption]
Traumatic optic neuropathy--Sudden amaurosis as a aftereffect of a horse falling over astern and traumatizing the top of his skull can occur. This alarming optic neuropathy after-effects from disturbing of the affiliation tissue accoutrement the optic nerve, or absolute compression of the optic assumption associated with drain or breach of the skull. In aboriginal stages, the optic disc ability either arise normal, or be red and swollen. There can be banishment of optic disc actual into the vitreous, and accelerated development of optic assumption decline is noted. If both eyes are affected, both pupils are aggrandized with no signs of eye pain. Immediate and advancing systemic non-steroidal and/or steroidal anti-inflammatory analysis can advice bottle eyes in some cases.
Sudden Amaurosis
Acute, abrupt amaurosis ability be associated with arch or eye trauma, ERU, glaucoma, cataracts, intraocular hemorrhage, optic neuritis, retinal detachment, or academician disease. Anew dark horses are acutely agitated, anxious, and can be dangerous. Horses convalescent from anesthesia afterward abatement of sighted eyes because of tumors or infection can be actual abashed and agitated in the postoperative period. Extreme affliction should be activated and the animals approached carefully on the anew addled surgical ancillary until the horse adapts to his condition. Horses can acclimate amazingly able-bodied to blindness, whether in one eye or both eyes, if accustomed time to adjust. Several web sites are adherent to the affliction of dark animals. Simply blazon "blind horses" into an Internet chase engine.
Editor's note: This is the twelfth in a alternation of eye accessories by Dr. Brooks. See the aboriginal article, "Eye Analysis and Physiology," commodity #2797 at www.TheHorse.com, for added advice on accustomed eye anatomy.
Dennis E. Brooks, DVM, PhD, Dipl. ACVO, is a assistant of ophthalmology at the University of Florida. He has lectured extensively, nationally and internationally, in allusive ophthalmology and glaucoma, and has added than 140 refereed publications. He is a accustomed ascendancy on basset glaucoma, and communicable keratitis, corneal transplantation, and glaucoma of horses.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="288"][/caption]
Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs - differentials for epistaxis in dogs
| Encouraged to be able to our weblog, on this time I will teach you concerning keyword. And after this, this is actually the 1st image:
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
 A Case Of Canine Trypanosomosis With Epistaxis In A TwoYear Old Alsat… | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
A Case Of Canine Trypanosomosis With Epistaxis In A TwoYear Old Alsat… | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
What about graphic over? is actually that will amazing???. if you're more dedicated so, I'l l explain to you several photograph yet again down below:
So, if you wish to obtain the outstanding graphics related to (Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs), press save icon to save these pics for your computer. They're ready for download, if you like and wish to own it, simply click save symbol on the post, and it will be directly saved in your laptop computer.} As a final point if you would like grab new and the latest picture related to (Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs), please follow us on google plus or save this website, we try our best to give you regular up-date with all new and fresh graphics. Hope you like staying here. For some upgrades and recent information about (Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs) shots, please kindly follow us on twitter, path, Instagram and google plus, or you mark this page on bookmark section, We try to provide you with up grade regularly with fresh and new shots, enjoy your searching, and find the right for you.
Here you are at our website, contentabove (Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs) published . At this time we are pleased to declare that we have found an incrediblyinteresting nicheto be reviewed, namely (Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs) Lots of people looking for details about(Understanding The Background Of Differentials For Epistaxis In Dogs. | differentials for epistaxis in dogs) and definitely one of these is you, is not it?[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="288"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
 Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
 Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
Differential diagnosis in small animal medicine | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="795"]
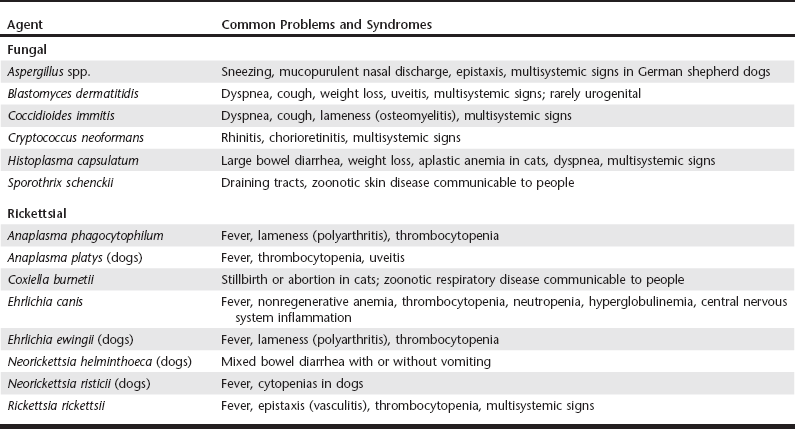 Infectious Agent Differentials for Medical Problems | Veterian Key | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
Infectious Agent Differentials for Medical Problems | Veterian Key | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"]
 Nose Bleeds or Epistaxis in Dogs | VCA Animal Hospital | differentials for epistaxis in dogs
Nose Bleeds or Epistaxis in Dogs | VCA Animal Hospital | differentials for epistaxis in dogs[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="480"]
[/caption]